Past. Present. Future. These are the three tenses that structure time. But what are the tenses of a verb? And more simply: what is a verb tense? Fear not, we’re going to answer those questions, as well as break down all twelve types of verb tenses. By the end, you’ll know what a verb tense is and how to identify the correct one for each use-case.
Past Tenses, Present Tenses, and Future Tenses
First, let’s define grammar aspects
We have established that there are three tenses: past, present, and future. But verb tenses don’t just utilize tenses – they utilize grammar aspects as well.
What are grammar aspects? Grammar aspects (or grammatical aspects) are components of language that clarify the length of duration for an action.
For example: “I raked the leaves yesterday,” and “By tomorrow, I will have been raking the leaves for two days straight” communicate different durations of time for the same action.
This next video from TED-ed examines some of the basics of verb tense in greater detail.
What are the Tenses of a Verb? • How Many Tenses in English by Anna Ananichuck and TED-ed
There’s no doubt about it: verb tense is ingrained into the English language. Any and all aspiring learners ‘ought to consider all the types of verb tenses in order to properly communicate their ideas. But before we get too far into the intricacies of verb tenses, let’s formally define verb tense and its twelve types.
VERB TENSE DEFINITION
What is a verb tense?
A verb tense is a way of referring to an action at a point in time: past, present, or future. Verb tenses are further distinguished by descriptions of how long an action has taken, is taking, or will take.
12 Verb Tenses
- Past Simple
- Present Simple
- Future Simple
- Past Continuous
- Present Continuous
- Future Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Present Perfect
- Future Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect Continuous
What are the Tenses of a Verb?
What are some verb tense examples?
Verb tenses may seem challenging to identify, but they are something we instinctively interpret and implement in our everyday lives. That’s because we are conditioned into seeing things temporally (in terms of time); it’s how we make sense of our world and the things around us.
When somebody asks us if we did something we were planning to do, we usually respond in one of three ways:
Yes, I did
No, I am doing it
No, I will do it in the future
These are the most common (and basic) ways of communicating verb tense. However, there are many more! Let’s break down each, using the infinitive verb “to play.”
PAST TENSES
There are four different ways of describing actions in the past.
Past Simple:
Actions that happened and were completed in the past.
For example: I played basketball last weekend.
Past Continuous:
Ongoing actions that began in the past.
For example: I was playing basketball on weekends.
Past Perfect:
Actions in the past that took place before or after other actions in the past. For example: I had played basketball until it got too dark to see the ball.
Past Perfect Continuous:
Ongoing actions in the past that have a correlatory relationship to other events in the past.
For example: I had been playing basketball while living in the city.
PRESENT TENSES
There are four different ways of describing actions in the present.
Simple Present:
Actions that are happening in the present; connect to the infinitive version of the verb.
For example: I play basketball.
Present Perfect:
Actions that began in the past but are still happening in the present.
For example: My friends have played basketball for years.
Present Continuous:
Ongoing actions that are happening in the present.
For example: I am playing basketball.
Present Perfect Continuous:
Ongoing actions that are happening in the present but that began in the past.
For example: I have been playing basketball for a few hours.
FUTURE TENSES
There are four different ways of describing actions in the future.
Future Simple:
Actions that haven’t happened yet.
For example: I will play basketball next weekend.
Future Continuous:
Ongoing actions planned for the future.
For example: I will be playing basketball this weekend.
Future Perfect:
Actions planned to be completed at some point in the future.
For example: By Sunday, I will have played my last basketball game.
Future Perfect Continuous:
Ongoing future actions that correlate to current or past timeframes.
For example: I will have been playing basketball for twelve weeks by Sunday.
And here is a chart for looking at all twelve verb tenses:
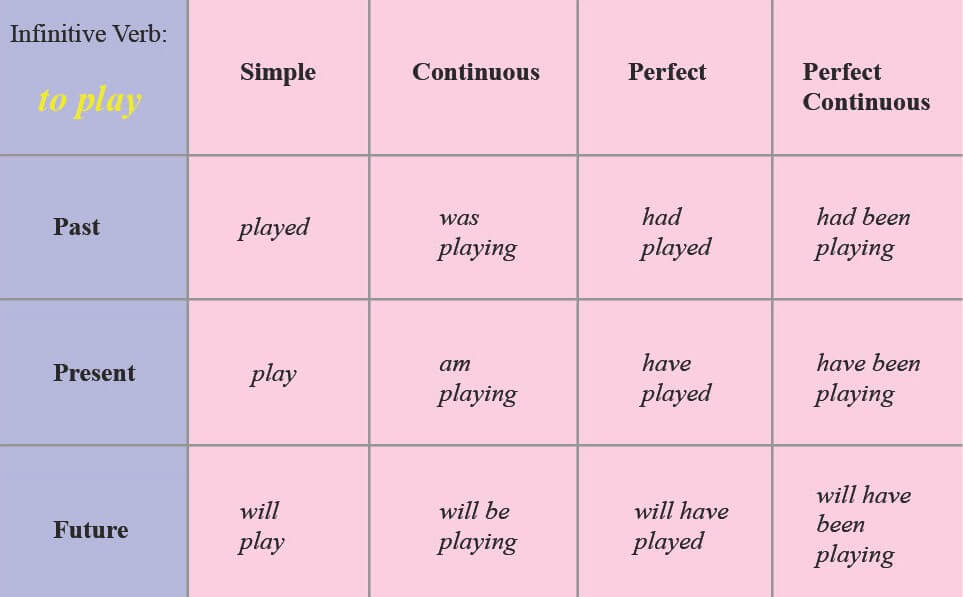
What are the Tenses of a Verb? • Verb Tenses Chart
You can plug in just about any regular verb into this chart. However, irregular verbs abide by different rules. For example: the irregular verb “give” would have multiple past participles, such as “gave” and “given.” This would change the verb tenses to “gave,” “was given,” “had given” and “had been given.” The present and future simple tenses will use the infinitive version of the verb derived from “to give;” the rest of the verb tenses will use “given.” In this case, the past simple verb tense does not match the rest of the chart.
What are the Tenses of Verb Used For?
Why verb tenses are important
Tense is both a technical and creative concern for writers. The correct implementation of verb tenses ensures proper syntax and grammatical clarity. So, technically, it is essential that you utilize the right tense. However, you can choose what tense to use in your own writing. In this video, author Brandon Sanderson says that “it doesn’t matter” what tense you use when writing fiction (at least from a structural level).
What are the Tenses of a Verb? • Choosing Past or Present Tense, by Brandon Sanderson
Of course, you still need to match tenses, no matter whether you’re writing about the past, present, or future. Writers often mismatch tenses improperly. For example: in the sentence “I went to the store and buy groceries” the two verbs, “went” and “buy” are not the same tense. The sentence should read either a) “I went to the store and bought groceries” or b) I will go to the store and buy groceries.” Tense-shifting is one of the most common mistakes writers make.
Make sure to match tenses in your own writing to ensure you are properly communicating with your reader(s).
Up Next
What is a Complex Sentence Structure?
Verb tenses are just one component of grammar. Want to learn more about writing perfect English? Check out our next article on complex sentence structure where we break down syntax in structure with examples from Field of Dreams and more. By the end, you’ll know what complex sentence structure is, and how to identify it in writing.
