S
hooting projects on a budget can mean limitations on your gear. So how can you maintain a “cinematic” look without a cube truck full of lighting equipment? In today’s post, we’ll examine what exactly it means to have a cinematic look. Then we’ll break down several lighting techniques that are achievable on any budget. Although cinematic lighting is predicated on creative interpretation, these principles of film lighting can form the basis of your creative choices. To show this, we’ve taken several examples of how the best DPs (directors of photography) create specific cinematic effects with thoughtful lighting setups of their own. Prepare to be inspired!
FILM LIGHTING TECHNIQUES
1. Cinematic types of lighting in film
Every cinematographer is an artist who makes creative decisions on how to guide the viewer’s eye within the frame using lighting equipment.
Their applications are broad, but their creative interpretation is what makes their lighting cinematic (or not). They include:
- Which props and scene elements should be emphasized
- Whose perspective we’re seeing the scene through, and how much light they should be able to see
- How characters differ from one another in a frame
- Which emotions are being expressed through harshness of light, or its color
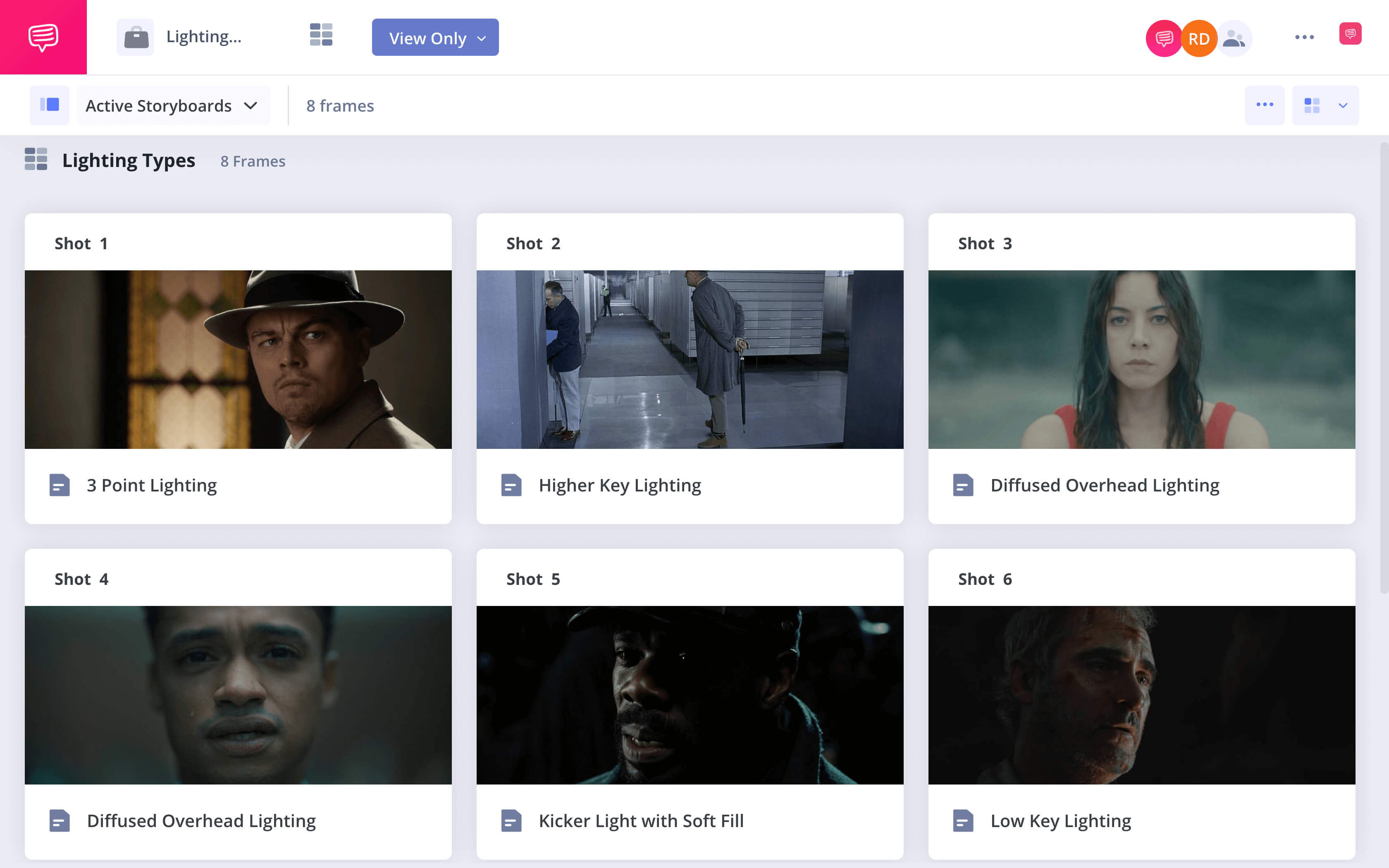
Lighting Types
Each of these decisions are then realized technically by planning and executing lighting setups to create the desired effect. But the cinematographer must dream up what these effects will be before setting up any lighting equipment.
Free downloadable bonus
FREE Download
Ultimate Guide to Exposure
The Exposure Triangle is something every photographer and cinematographer needs to master. Download our FREE e-book to get in-depth explanations and tutorials on topics like aperture, ISO, shutter speed, and how to balance these settings to nail perfect exposure every time.
Film Lighting Techniques
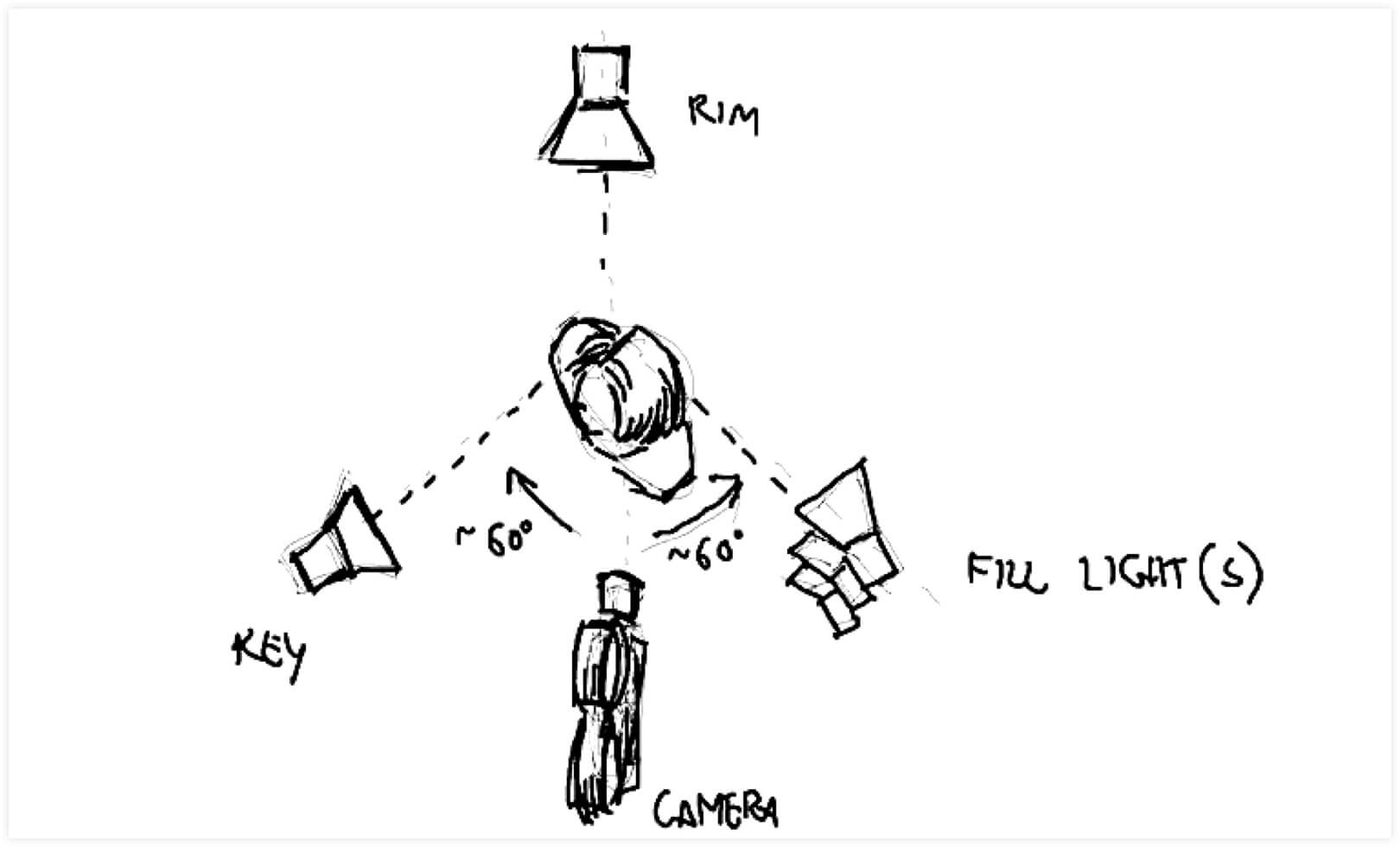
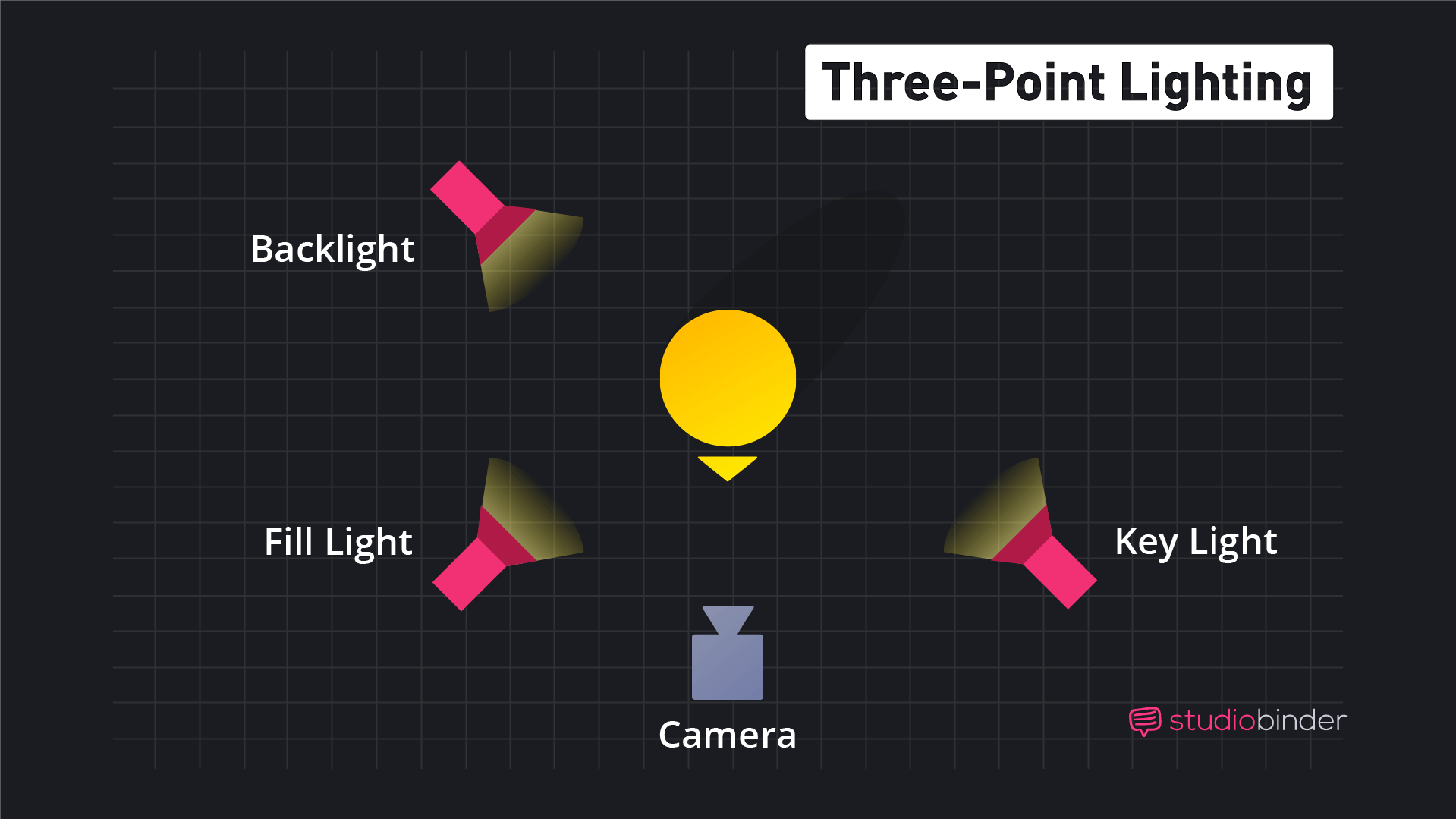
2. Basic lighting: 3-point lighting setup
The most basic lighting in film is the three-point lighting setup. Lighting from three directions shapes your subject and sets them apart from their background.
To achieve this, your film lighting equipment needs to face your subject from three directions: front, back and side (generally).
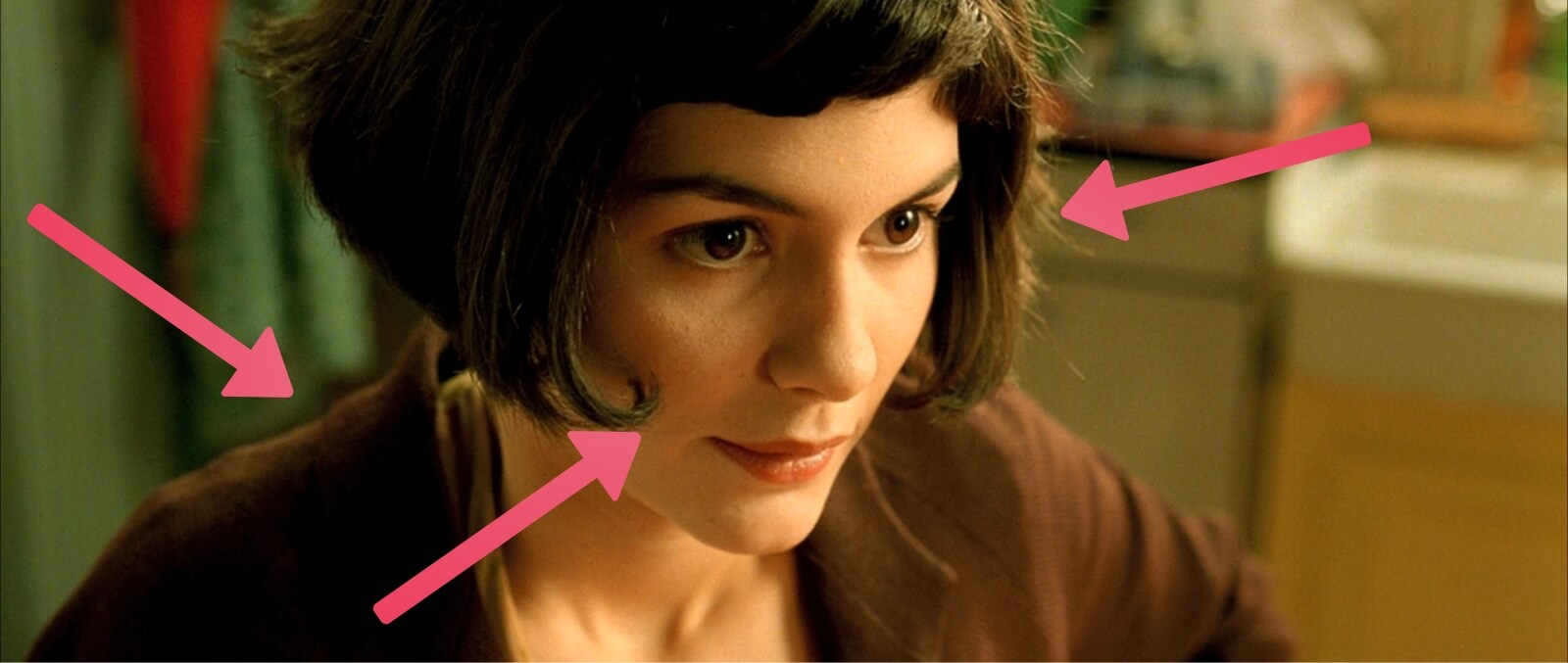
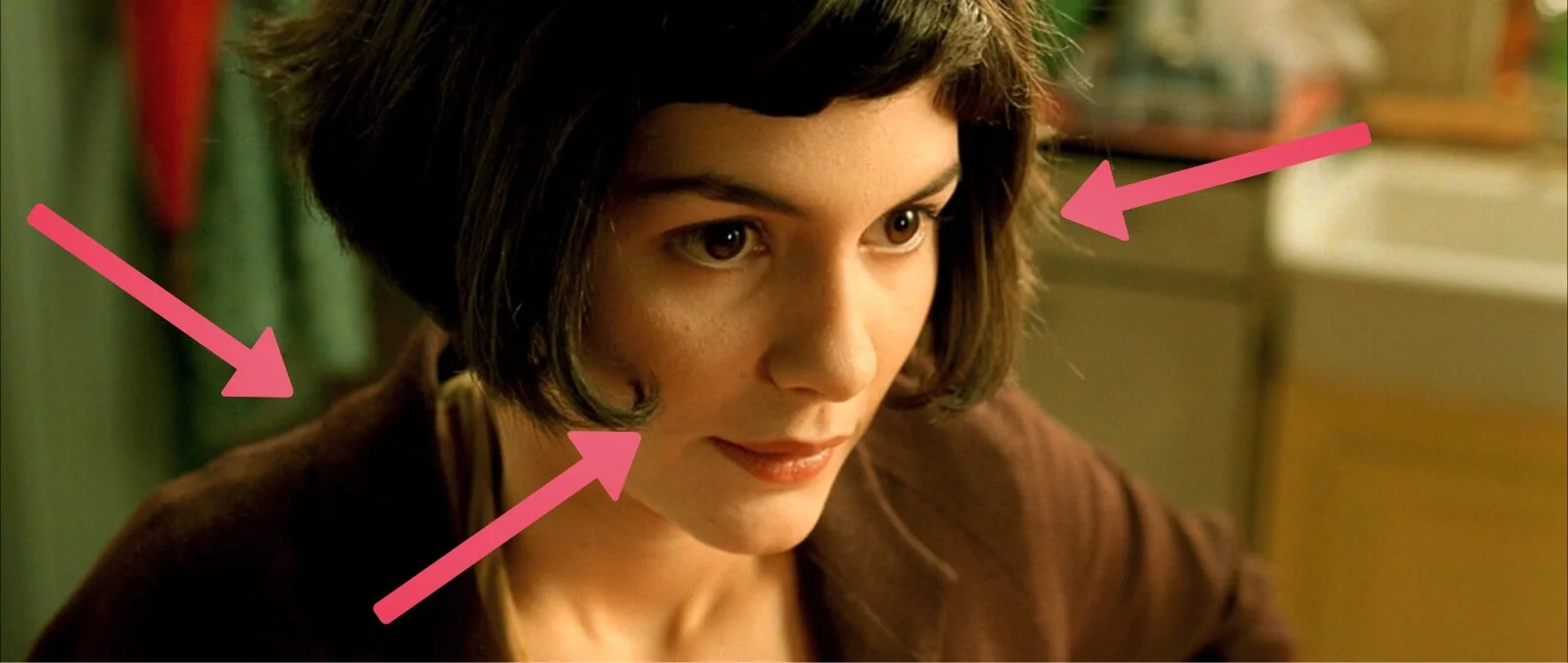



Film lighting basics: Amelie (2001), using the three-point lighting setup
KEY LIGHT
The key light is the light that registers most prominently in your frame. So, when you look at the image of Amelie above, you’ll see that the screen-right portion of her face is brightest. That’s the key light.
FILL LIGHTS
Quite simply, fill lights fill in the shadows of your frame. You’ll notice that the screen-left portion of Amelie’s face is in shadow, but with her features still plainly visible. That is a fill light at work.
BACK LIGHT
The back light gives an edge light to the rear portion of your subject. Often, the backlight shoots down from a higher angle. You can see that Amelie has a light contour along her shoulders and the nape of her neck.
You’ll generally want to flank your camera with your key and fill lights, spaced about 60 degrees on an axis from your camera.
Basic lighting techniques: Back, Key, and Fill lighting arranged around a camera
Related Posts
FILM LIGHTING TECHNIQUES
3. Soft film lighting
When talking about how a scene should feel emotionally, one thing that is referenced by cinematographers frequently is how hard or soft lighting should be.
The hardness or softness of light concerns how large a light source is, and how it affects shadows on your subject.
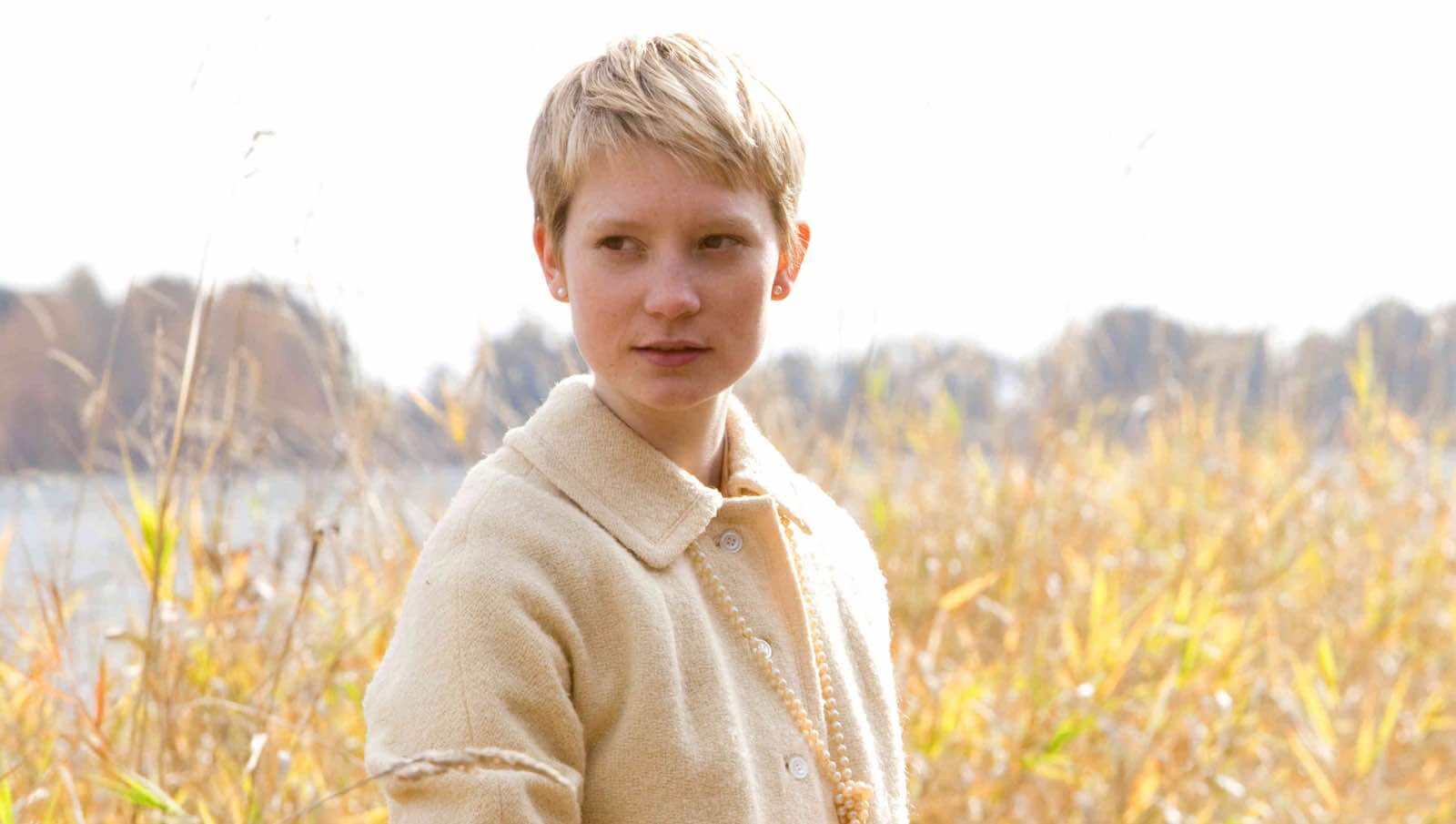
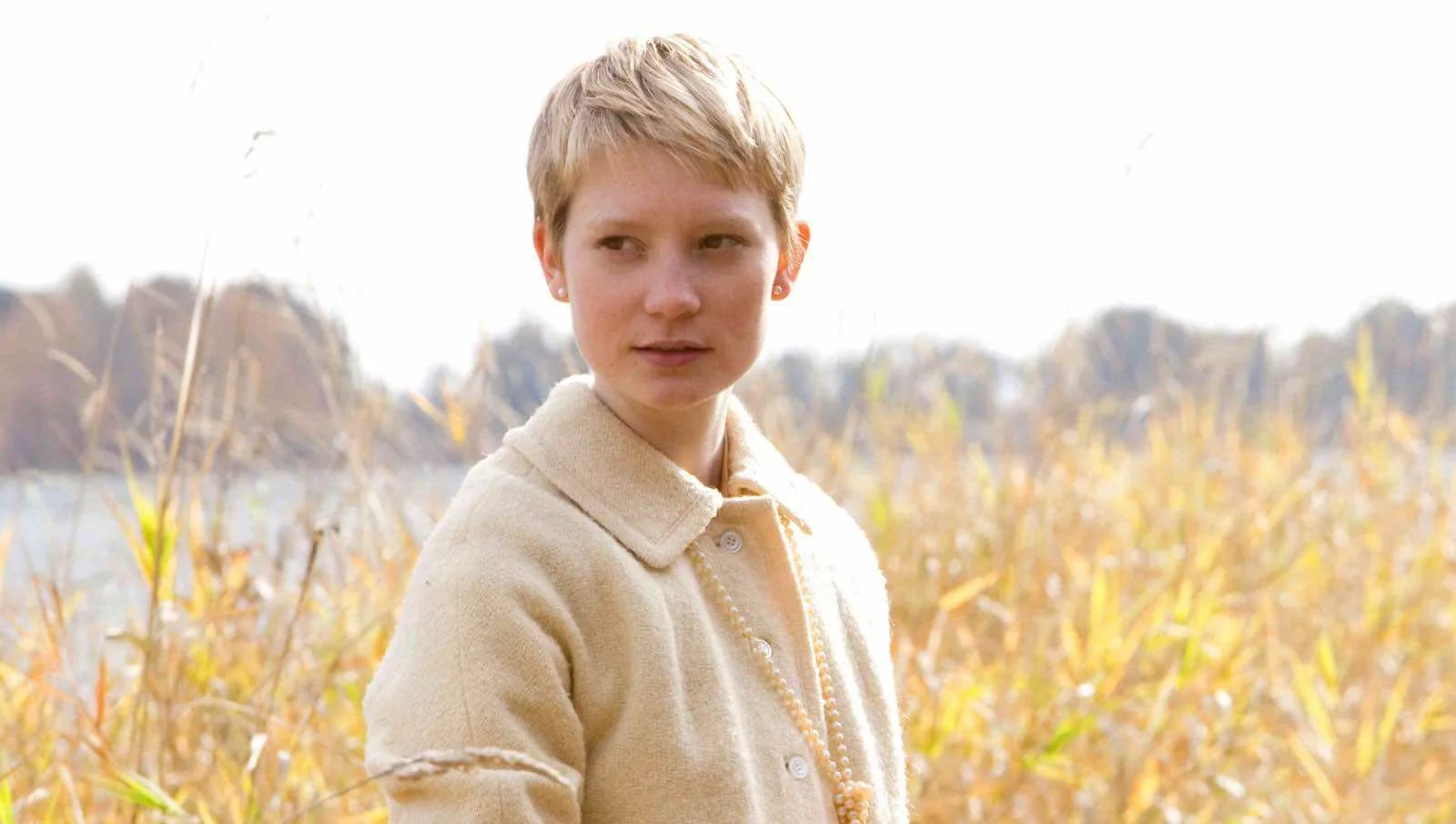



Soft film lighting in a day exterior in Restless
HIGHER KEY LIGHT
This is an effect created by heightening the key light and using fill lights generously. This keeps the lighting bright and balanced in your frame, creating almost no shadow. This balances the lighting from object to object in your frame — which is known as your lighting ratio.
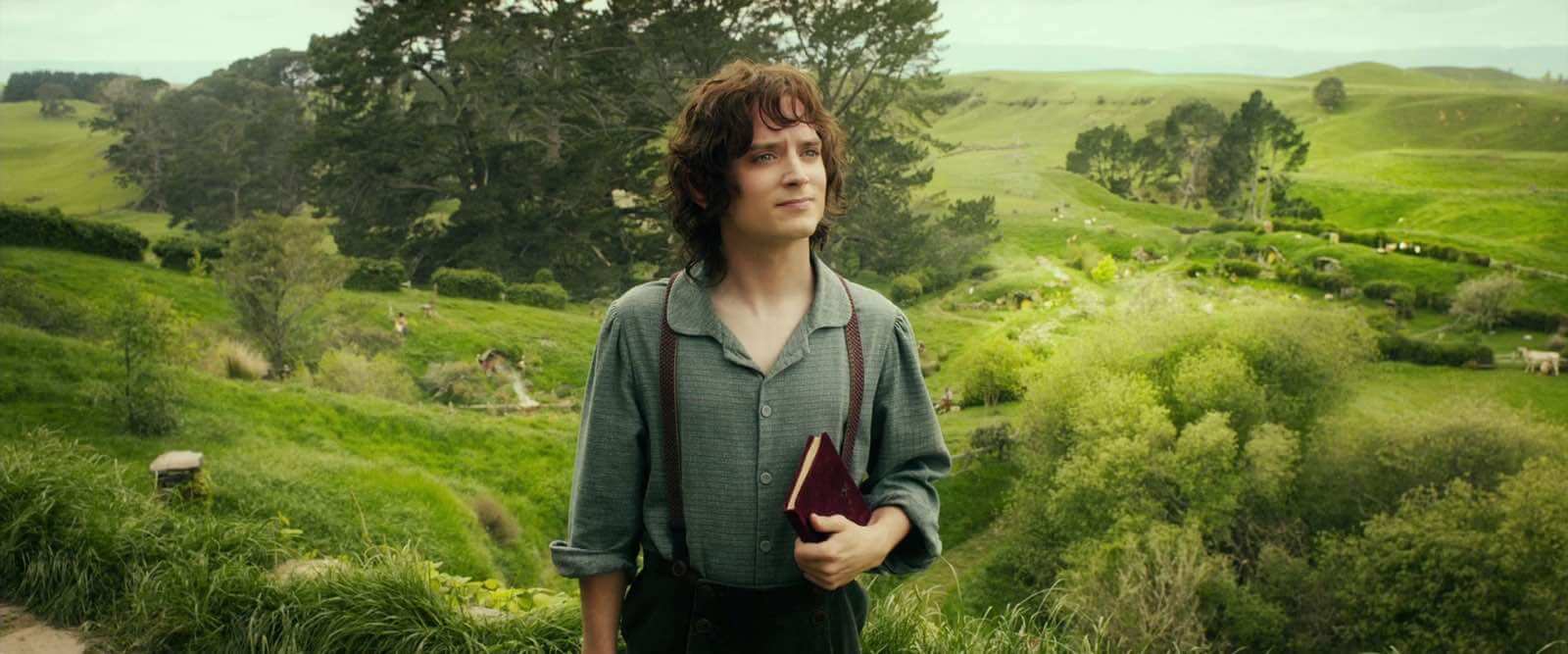
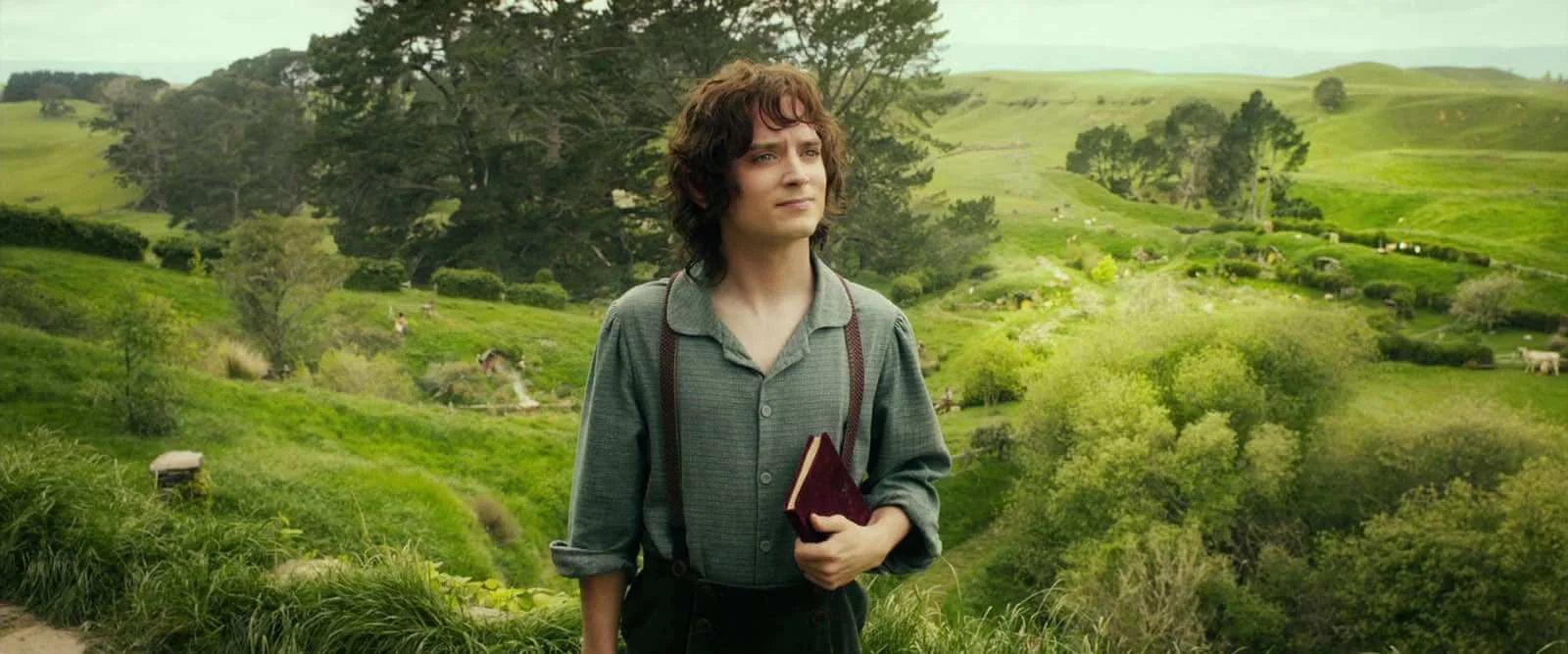



High key film lighting in The Hobbit
DIFFUSED OVERHEAD LIGHTING
You can soften a light source with diffusion materials like gels or Chinese lanterns to reduce shadows. This is great for shooting close-ups.
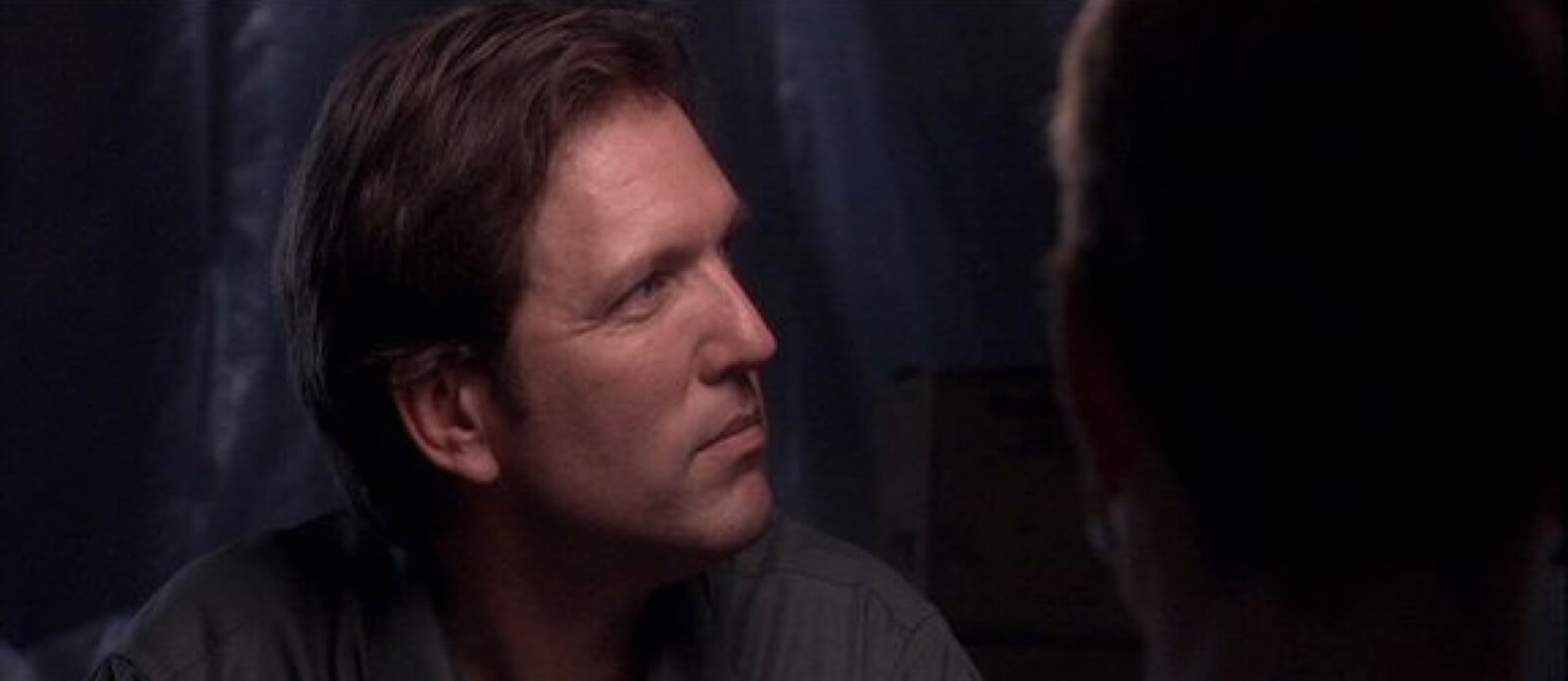
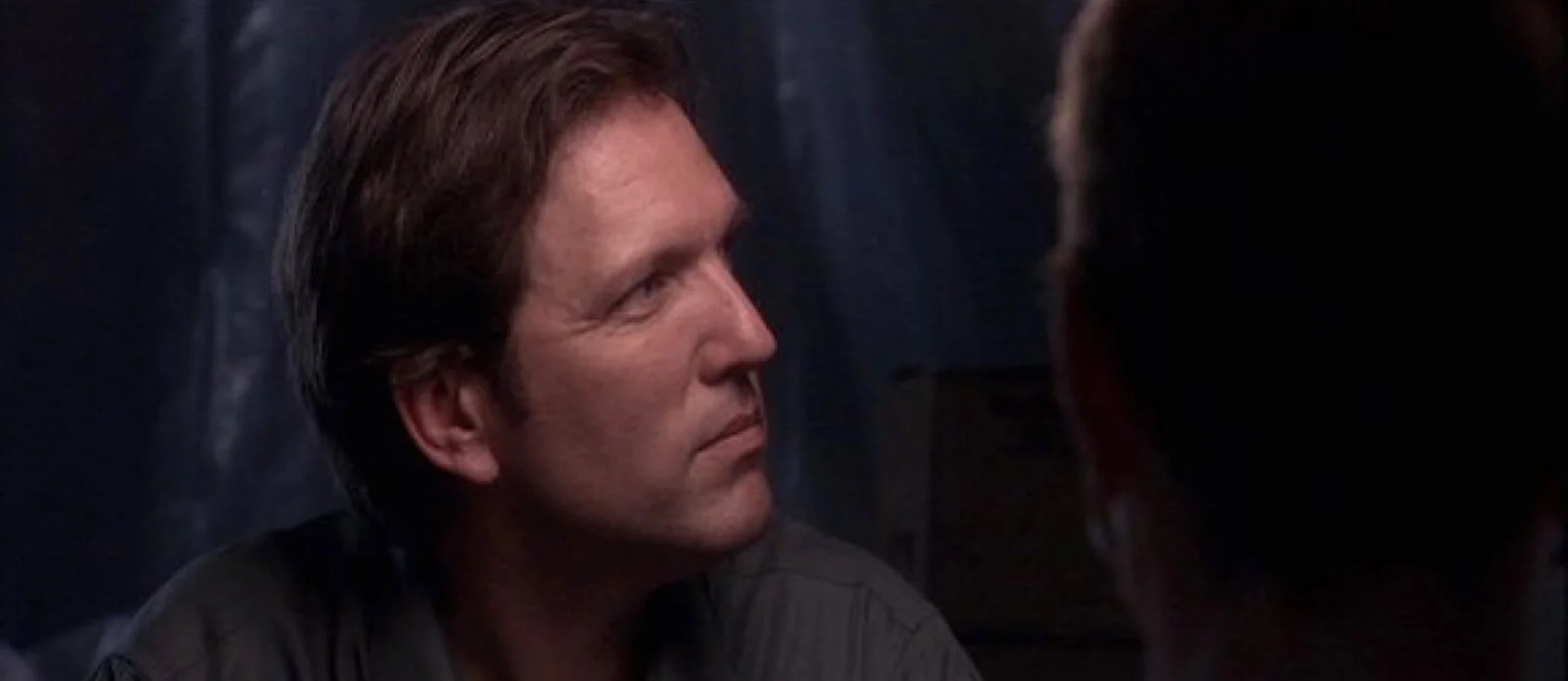



A Chinese lantern lights this close-up in The Quiet
FILM LIGHTING TECHNIQUES
4. Hard film lighting
Conversely, smaller light sources, including bright sunlight, will heighten the shadows on your subject. Conservatively, this should be avoided. But it can also create dramatic effects, as was popularized in the classic Film Noirs, which featured suspicious and volatile characters.
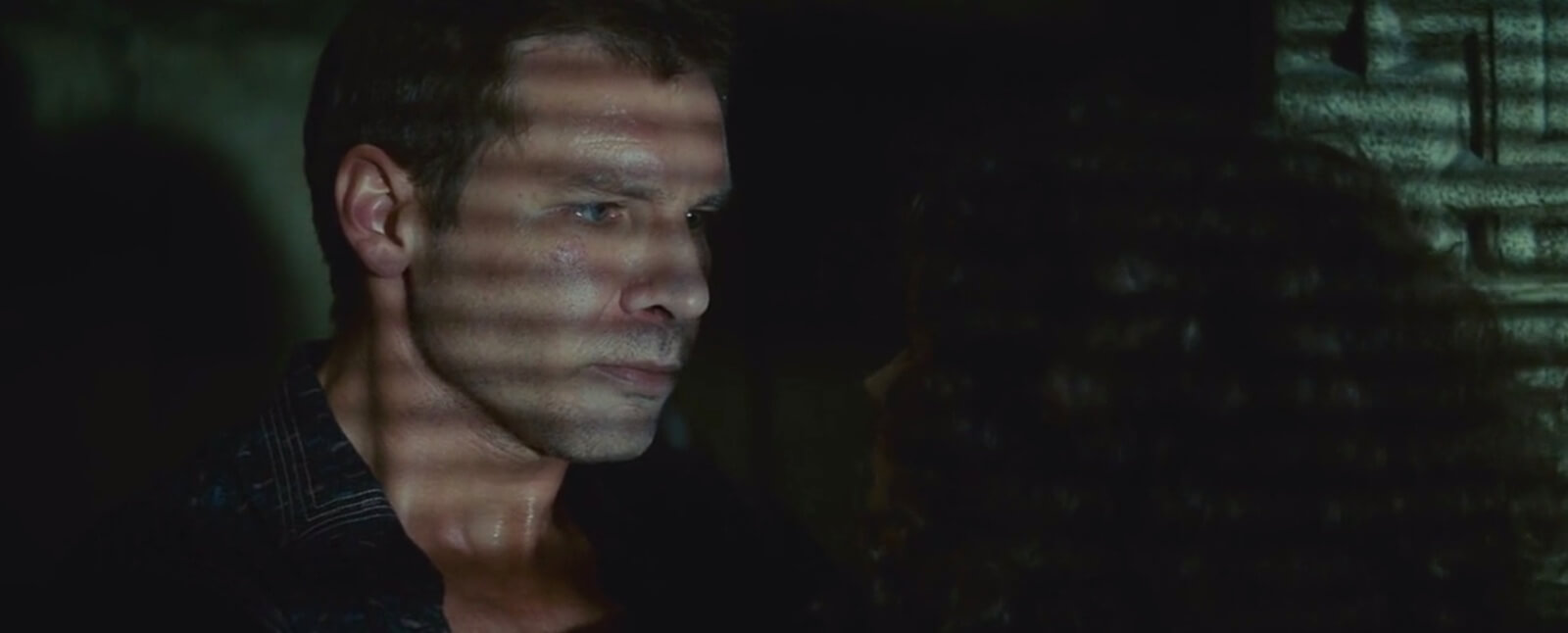



Hard lighting creates harsh shadows in Blade Runner's film lighting
KICKER LIGHT WITH SOFT FILL
In this effect, the back light hits the side of your subject’s face. It can create an angelic rim of light, while a very soft fill light keeps the face gently illuminated.



An angel-to-be receives an angelic kicker light in Northfork
LOW KEY LIGHT
Low key lighting refers to minimizing, or eliminating, the fill light your shot so that it is intentionally shadowy. This can create dramatic, suspicious, or even scary effects.
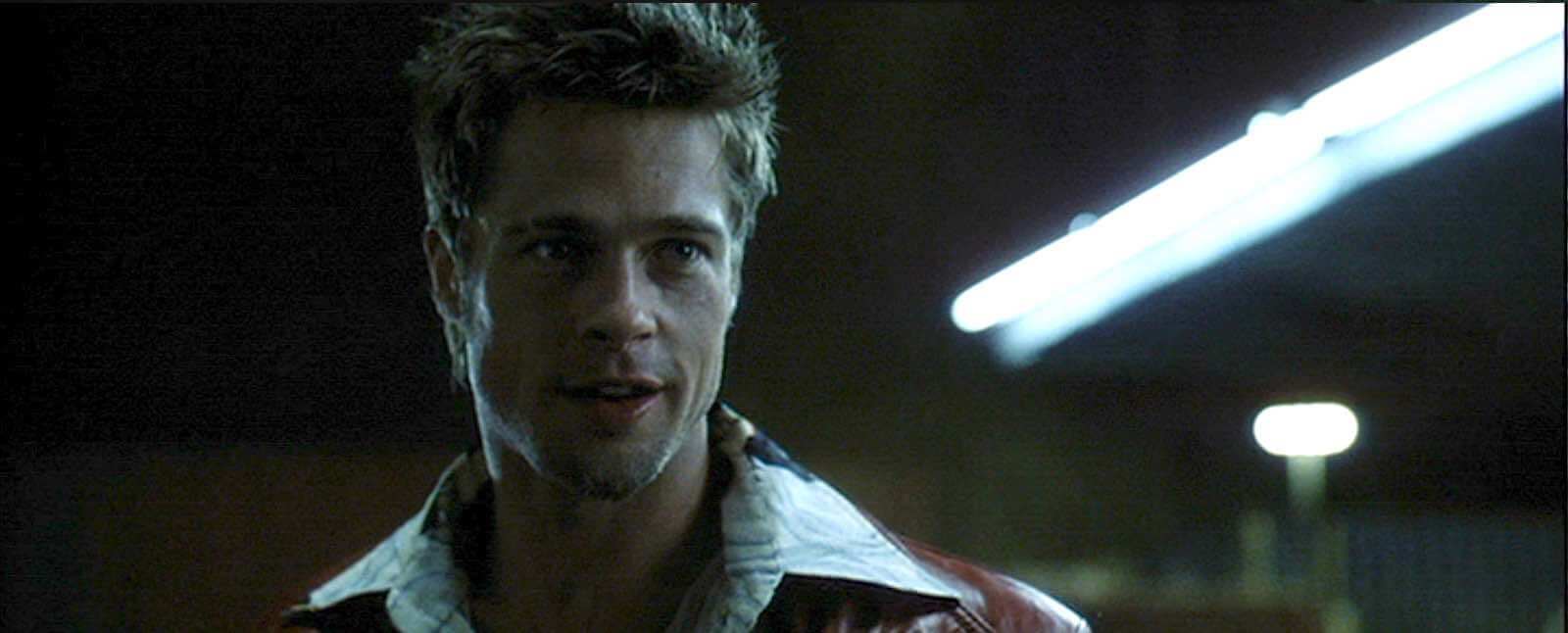
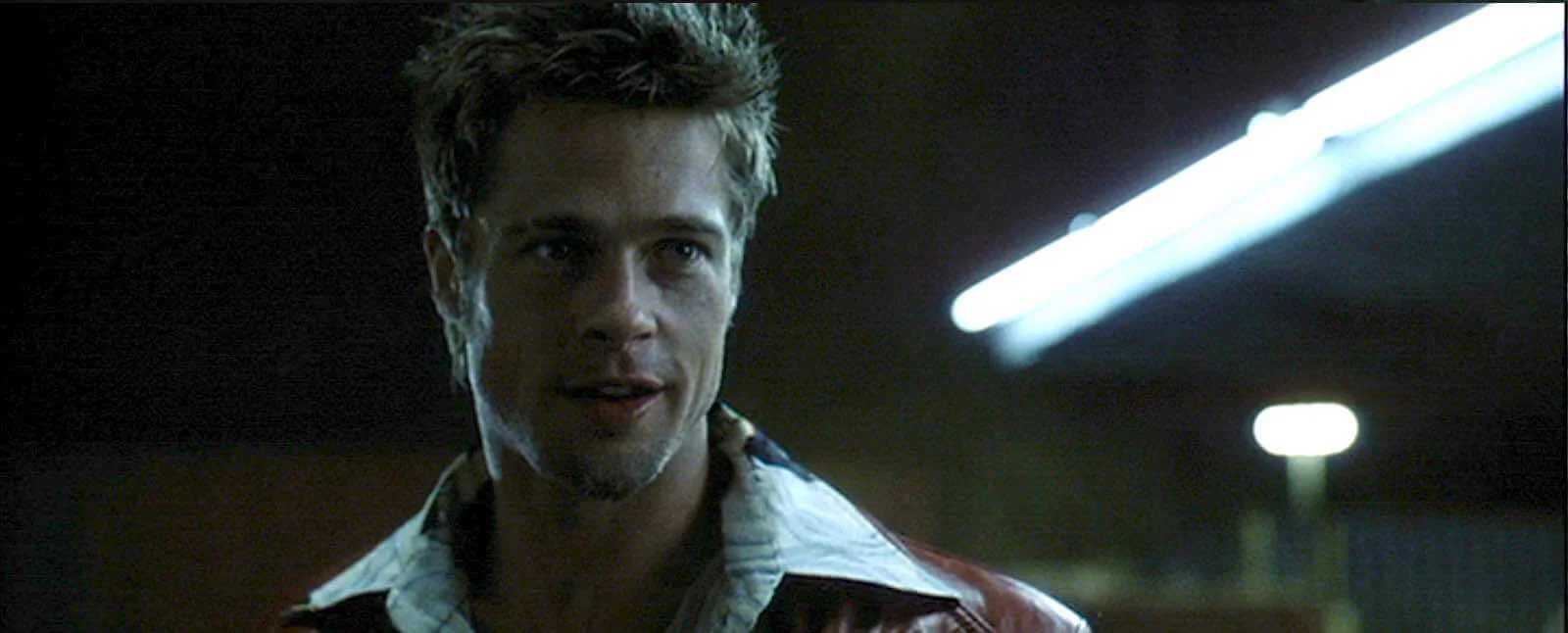



Among the types of lighting in film, low key lighting is great for mystery
Related Posts
FILM LIGHTING TECHNIQUES
5. Motivated lighting
When cinematographers light a set, they always ask themselves where, within the scene, the light comes from.
They might, for example, choose to take the practical lights that are already in a location and elevate their effect. This is motivated lighting.
Motivated Lighting • Subscribe on YouTube
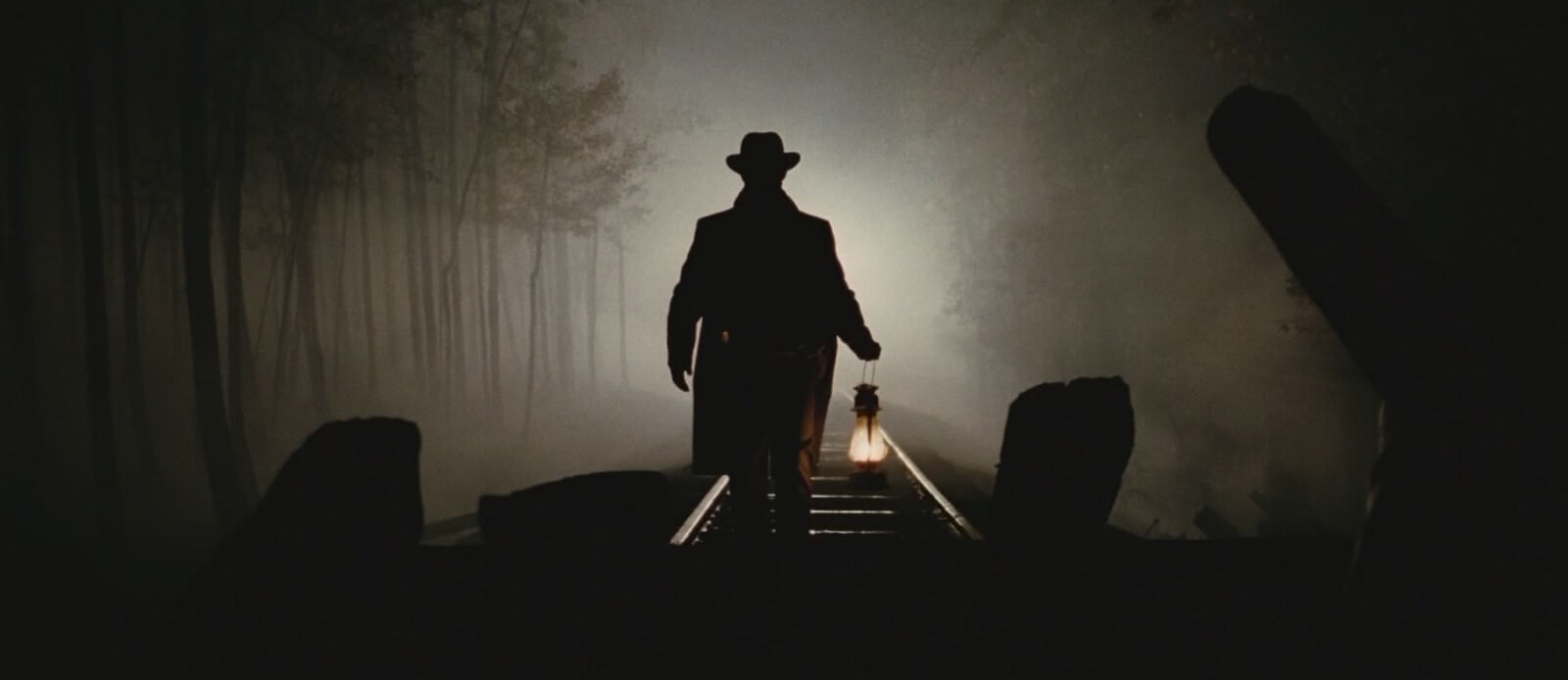



Motivated lighting in The Assassination of Jesse James
As you can see, the lighting in this scene is motivated by the lanterns carried by the actors. When motivated lighting is done right, the audience is unaware of the artifice at work.
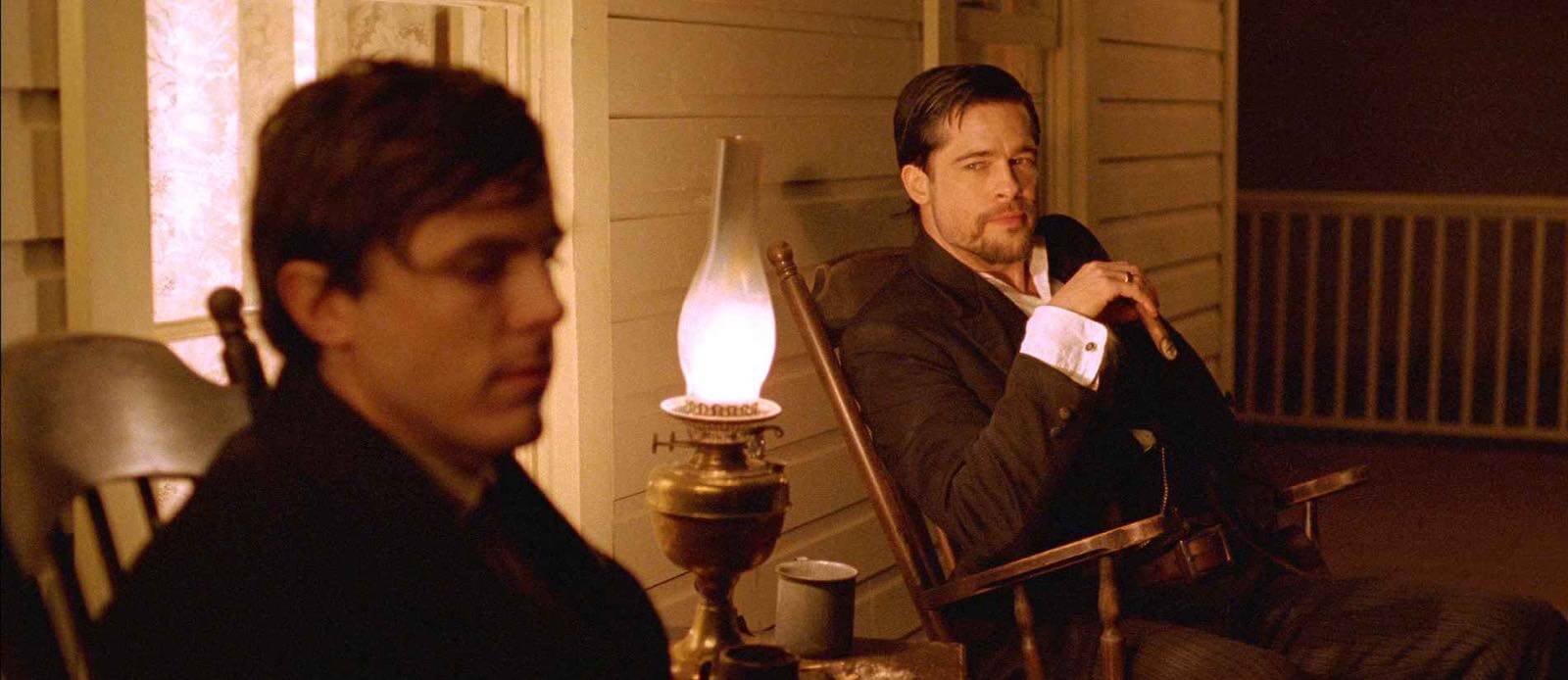
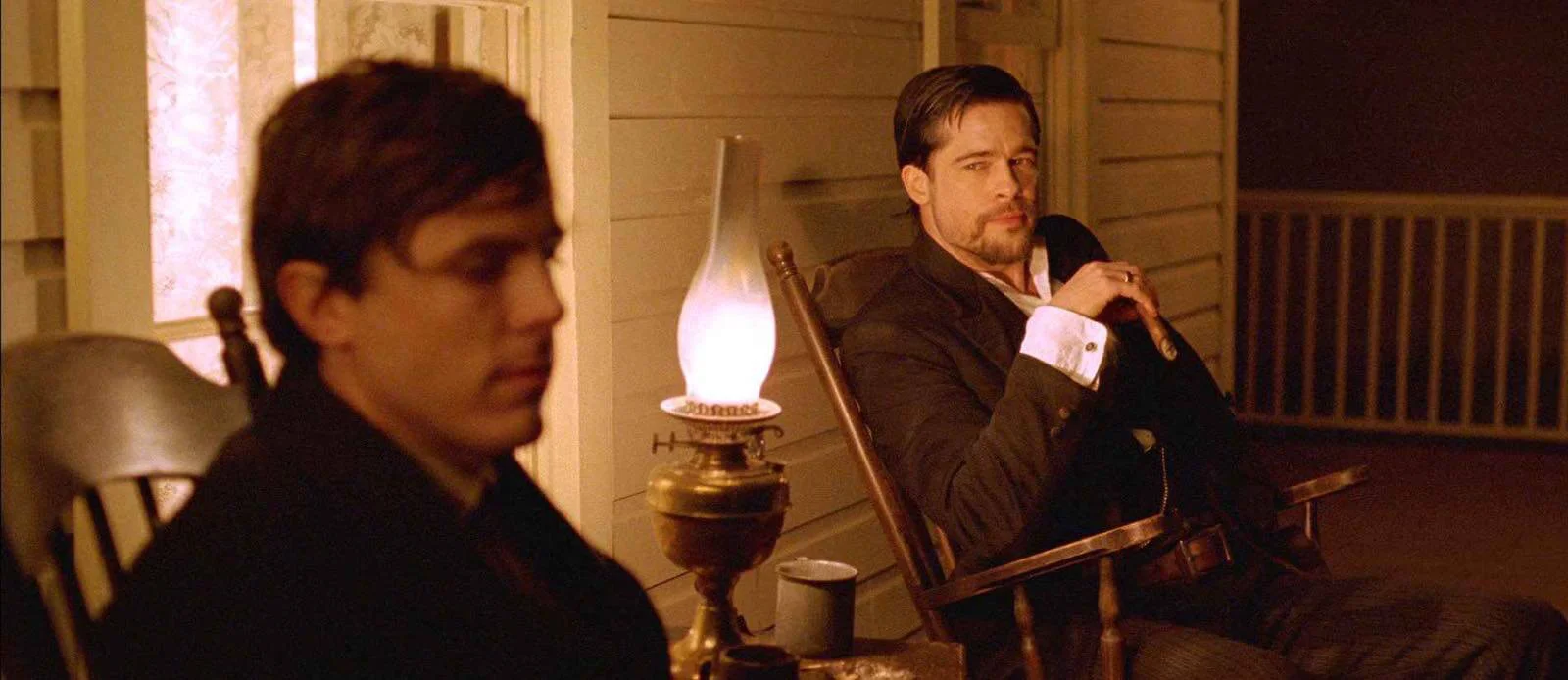



Lanterns create motivated light sources that sell the lighting choices
PRACTICAL SET LIGHTING
Often times, using existing lamps and light sockets around the set can be used to light a scene. This is referred to as practical lighting, and is particularly useful when you need to reveal wide portions of the set, or move around it in longer takes.



A practical overhead bulb lights the subjects
This was the case in the diner scene in Moonlight. In an interview for TIFF Originals, DP James Laxton spoke about how he used practical set lighting to keep his location visible in wide frames.
Moonlight • Film Lighting Techniques
In essence, he swapped out the bulbs in the existing light sources around the diner to make them stronger. Since the scene reveals wide portions of their location, he relied on the practical sources, with some of LED light mattes brought in as well for additional soft, balanced light.
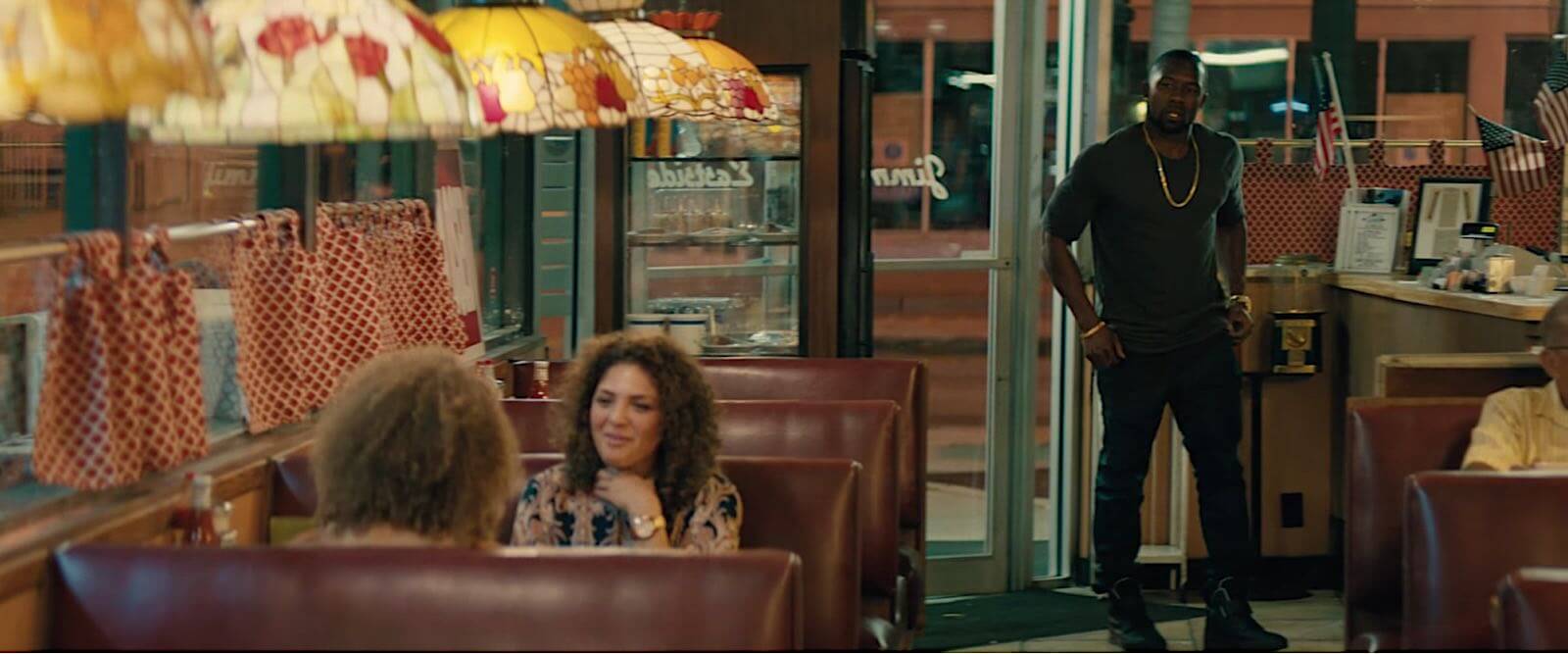

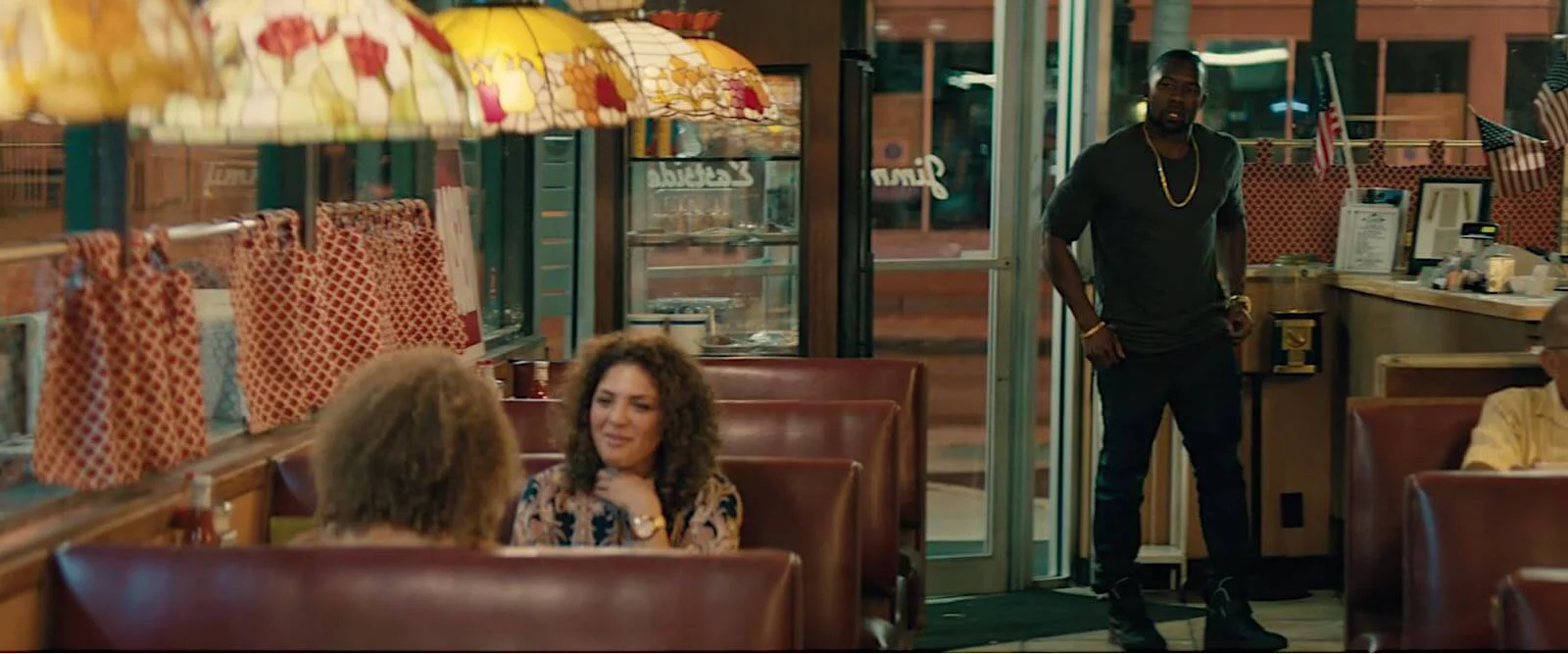
Practical lighting techniques at work in Moonlight
Here's Roger Deakins discussing his approach to practical lighting, and why "unmotivated" light always takes him out of the movie.
Deakins Talks Practicals • Subscribe on YouTube
FILM LIGHTING TECHNIQUES
6. Natural film lighting
Natural film lighting refers to using and modifying the light that is already available to you at your location.
Before you shoot, you can take your camera to the location to see how well the natural light holds up. You can decide from there how what additional lights you might need, or how you might adjust the light. For example, you can use bounce boards for reflecting the light, or black flags for blocking it out.
In this video, Deakins discusses how he first learned to pay attention to how natural light behaved — during fishing trips as a kid. Deakins is also a proponent of simplicity when it comes to lighting.
Roger Deakins Cinematography • Subscribe on YouTube
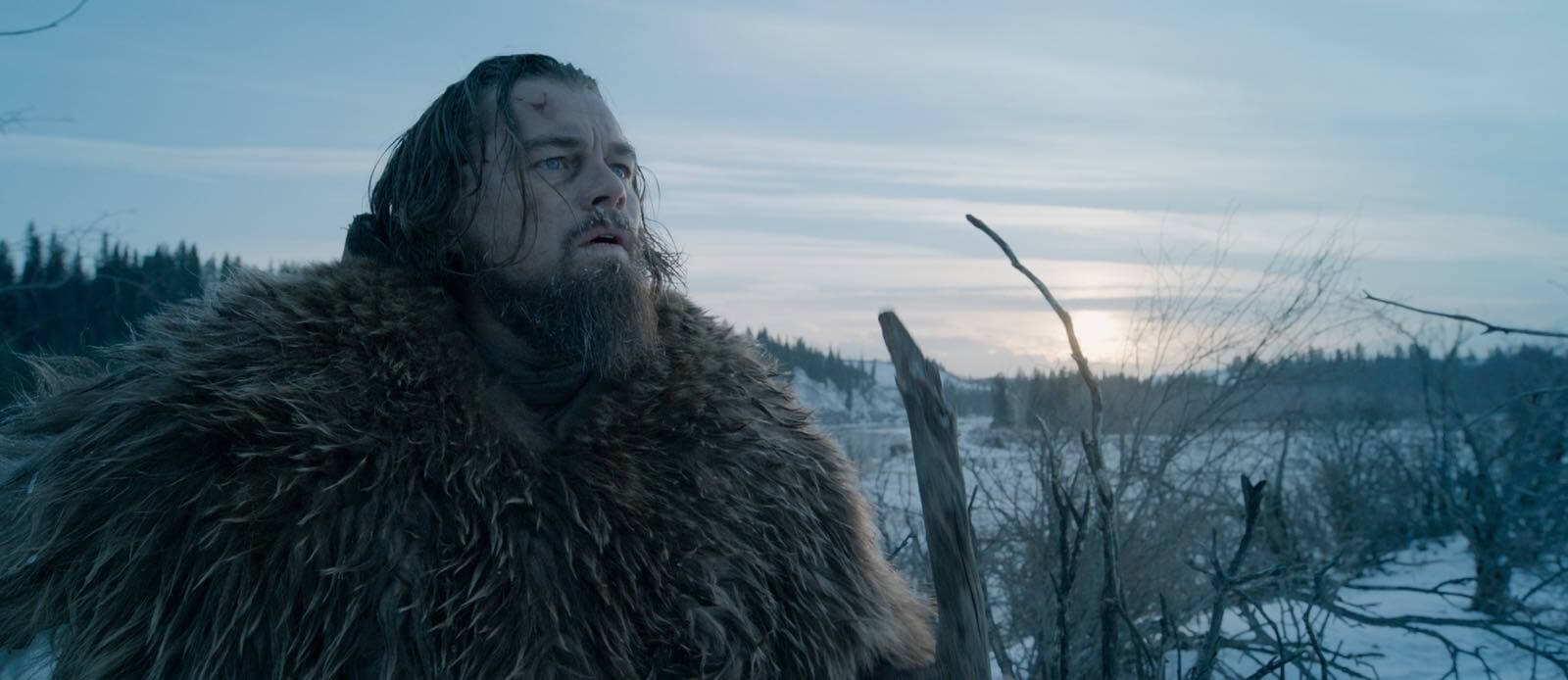



The Revenant created beautiful imagery with natural film lighting
For example, he speaks about using Magic Hour, or the soft light created by the sun at the end of the day, for specific moments. And, further, he talks about how the selection of locations, and how they appear at different times of the day, created appropriate moods for the shoot.
FILM LIGHTING TECHNIQUES
7. The set lighting technician's handbook and other good reads
Trade books can get you more comfortable with cinematography tools, common problem solving practices, and a deeper sense of how to make your vision actionable.
Here are a few that can be your lifesaver during pre-production and production:
SET LIGHTING TECHNICIAN'S HANDBOOK: FILM LIGHTING EQUIPMENT, PRACTICE, AND ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION
This guide puts you in the trenches of assembling lighting gear, with industry-standard techniques and hints to keep you sane during production.
SIGHT, SOUND, MOTION: APPLIED MEDIA AESTHETICS
This book takes you through the theory of creating visual imagery and how to apply them in modern production settings.
THE BARE BONES CAMERA COURSE FOR FILM AND VIDEO
A straightforward, affordable, and easy-to-understand guide to lighting and cinematography. It is a slim volume, but extremely thorough.
THE LITTLE BLACK BOOK OF LIGHTING FOR FILM AND VIDEO
Kino Flo is an industry standard light manufacturer who host this free film lighting techniques PDF on their website. Naturally, it is to be used in conjunction with their own equipment. But it takes you through many universal lighting tips for broadcast, documentaries and more.
Free downloadable bonus
FREE Download
Ultimate Guide to Exposure
The Exposure Triangle is something every photographer and cinematographer needs to master. Download our FREE e-book to get in-depth explanations and tutorials on topics like aperture, ISO, shutter speed, and how to balance these settings to nail perfect exposure every time.
RELATED POSTS
Up Next
Lighting tips you didn't learn in school
Like all aesthetic principles, lighting choices have highly individualistic interpretations, based on the DP or director. These techniques are purely meant to maximize cues that can create evocative imagery. For further reading, read about out how cinematography techniques, beyond lighting, that can enhance your storytelling. And, as always, be sure to let us know in the comments which techniques have worked well for your own shoots, and any we may have missed!
Up Next: Cinematography Techniques →
Share your vision with elegant shot lists and storyboards.
Create robust and customizable shot lists. Upload images to make storyboards and slideshows.